Evolution of Automated Computing devices
- Charles Babbage’s Analytical Engine
- ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer)
- IBM PC (8088)
Charles Babbage’s Analytical Engine
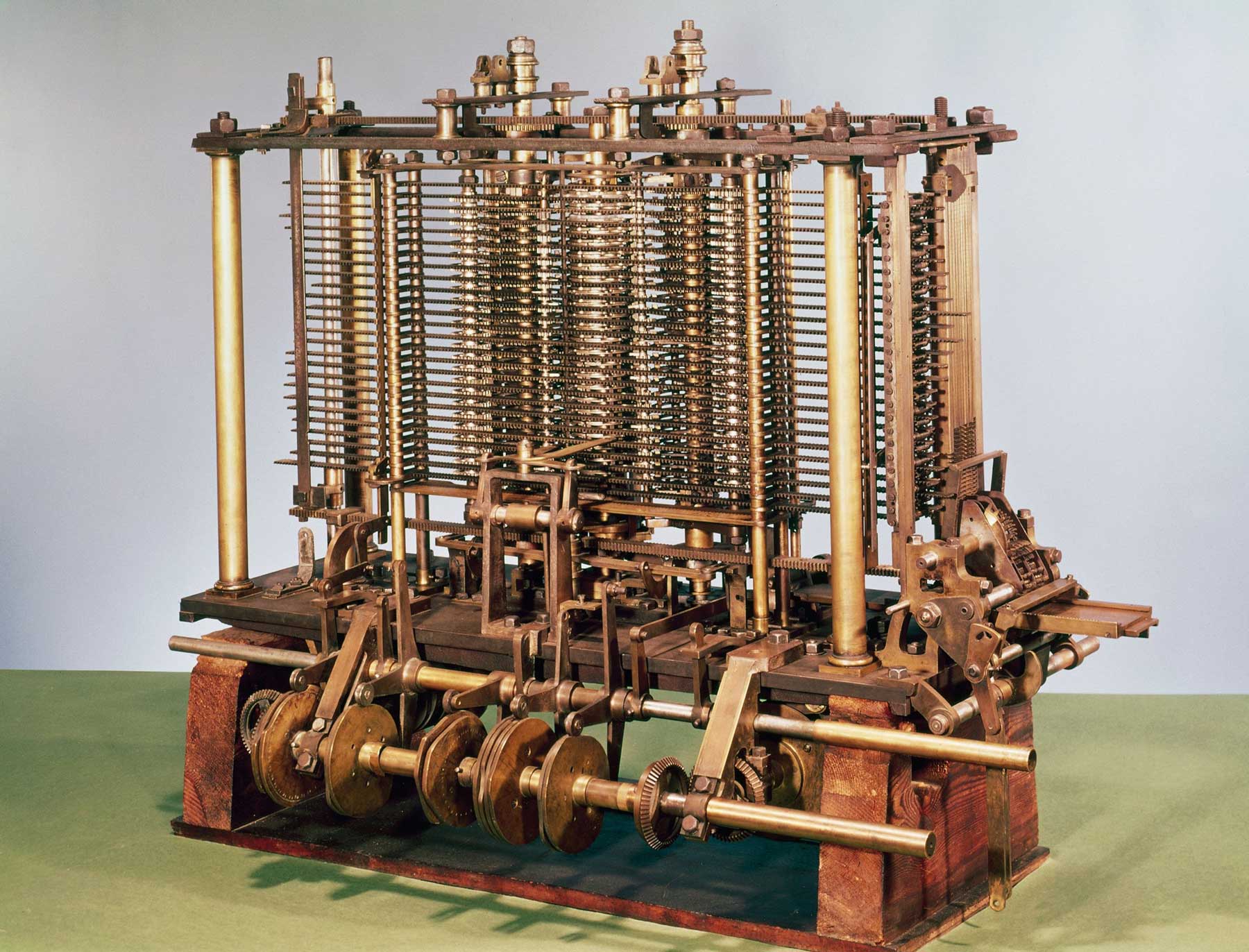 Charles Babbage created a theoretical, mechanical computing architecture powered by a steam engine
Charles Babbage created a theoretical, mechanical computing architecture powered by a steam engine
- Numerical values stored in human-friendly base-10 format
- Mechanical wheels store 10 different states. Modern transistors store 2 states for base-2 format.
- Upper limit of 40 digits to prevent overflow. No decimal support.
Anatomy of machine
- 40 wheels stacked on rotating vertical axis. 41st wheel denotes signage (even number = positive, odd number = negative).
- Axis stores system memory (store)
Addition operation
- Analogous to vertical addition.
- Two axis: Addend and Accumulator.
- Addend axis is connected to accumulator axis.
- Each addend digit is rolled down to 0, while the accumulator spins in the reverse direction to increase.
- If accumulator wheel hits 0, the next wheel (digit) increments, carries
Instruction Encoding
Stored by rotating barrels in a structure called the mill. Instructions coded by presence of studs. Locking was implemented to force wheels into correct positions and to reduce data transfer errors.
ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer)
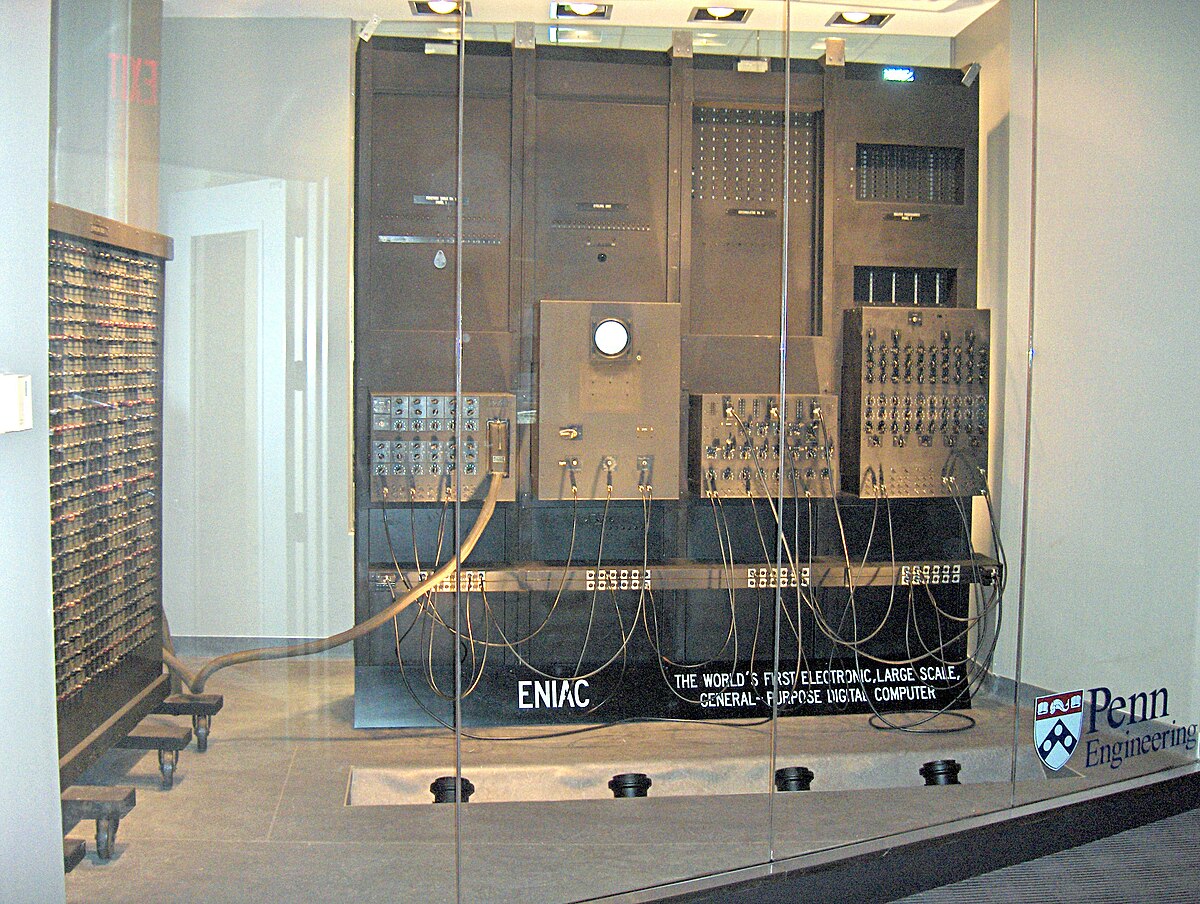 First programmable, general-purpose, electronic computer.
First programmable, general-purpose, electronic computer.
Machine Design
The only memory used by the computer were 10-digit accumulators (resembles the modern register)
- Vacuum tubes used as switches.
- Base 10 system like the Analytical Engine.
- Input received through punched cards. Modified by John von Neumann, who eventually created the modern von Neumann architecture.
IBM PC
IBM PC was inspired by various breakthroughs
- Invention of the transistor that provided speed and space optimizations for computations. More reliable than vacuum tubes.
- Widespread usage of Integrated Circuits (IC) by Texas Instruments that combined many components onto a single silicon chip.
- Intel’s first microprocessor (Intel 4004). Worked for 4-bit binary numbers.
8088 microprocessor
Specs:
- Clock freq: 4.77MHz
- RAM: 16kB (256kB expanded)
- Floppy Disks: 1-2
Comprised of 14 16-bit registers.
- 4 general purpose registers (AX,BX,CX,DX)
- 4 Memory Segment registers (CS,DS,SS,ES)
- served to expand addrses space to 20 bits
- Stack pointer (SP)
- Base pointer (BP)
- Source Index (SI)
- Destination Index (DI)
- Instruction Pointer (IP)
- Status Flags (FLAGS)
Input was fed through an external data bus of width 8 bits. Thus, two bus cycles were needed to write or read one 16-bit value. The processor had an execution speed of 0.3 million instructions per second (MIPS)
Implements the Von Neumann architecture as the program and data memory shared the same address space.
Instruction Set:
- Data movement
- Arithmetic, logical operations
- String manipulation
- control transfer (control flow for subroutines and jumps)
- I/O
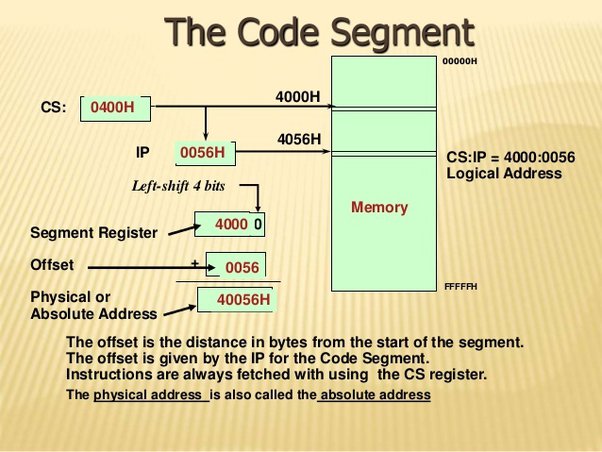
8088 expands the range of addressable memory space from 16-bits to 20-bits by the use of an offset value. The Segment registers represents the offset of the memory address, as each register represents a 64kB block of memory. This offset is added on to a 16bit physical memory address (which is shifted left by 4 bits) to get the final 20bit address.
The CS (code segment) register was used to fetch instructions and to perform subroutines and jumps.
The DS (data segnment) register was used for data transfer to and from memory
The SS (stack segment) register was used toallocate local memory from subroutines and also stores the return addreses of subroutines.
It is easy to store programs whose code, stack, and data segments were less than 64kB (as they can just be represented by each of the registers). However, for programs which sizes increased byond 64 kilobyte, 8088 compilers use near and far references to memory.
- Near Pointer: 16-bit offset from current segment register base address
- Far Pointer: 16 bit segment register value and 16 bit offset.
Programs that exceeded 64kB in data must be broken into chunks no larger than 64 kB and be micromanaged individually.
80286 and 80386 microprocessor
IBM released the PC AT (Advanced Technology) in 1984 that included the 80286 which used a 16-bit data bus which reduced the time required to write and read data. There were 24 address lines which could access a 16mB address space.
The 80386 had a 32bit processor that had 32bits of memory in a protected mode (One user’s program memory could not affect that of another’s in a multi-user operating system).
The iPhone

iPhone was released by Steve Jobs in 2007. Combined the portability of the iPod with the computing power of the Macintosh Computer. The iPhone supported the Global System for Mobile communication (GSM) which allowed for cellular communication. The iPhone 1 processor used a Samsung 32bit ARM11 processor. The processor supported Single Instruction-Multiple Data (SIMD).
Moore’s Law
Intel CEO Gordon Moore proposed Moore’s Law which predicted the growth of components that can be integrated on a chip will double each subsequent year. Often used to measure the performance of the semiconductor industry. Growth has been declining recent. The clock speeds of chips are higher as their are shorter paths between components with more components per die area. The speed of Moore’s Law decreases as the size of compoenents approaches their physical limits. An alternative to these physical limits is specialization. where certain circuit components are designed to perform a specific task really well rather than a variety of tasks. An example is the Graphical Processing Unit (GPU). GPUs focuses on efficiently completing repetitive computations, which is suitable for 3D graphics rendering and training Machine Learning models
Computer Architecture
Modern computers use varying voltage levels (low and high) to describe data values. Voltage that is interpreted by computers is thus analog.
Binary and Hexadecimal Numbers
The bit is the smallest unit of digital information, which is a discrete element of data measuring either 0 or 1. A collection of 8 bits can form a singular value called a byte which is also the smallest unit of information that can be read or written to memory in modern processors.